Introduction to Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for maintaining optimal health. It plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including bone health, immune function, and mood regulation. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the numerous benefits of Vitamin D3, its sources, recommended intake, symptoms of deficiency, and commonly asked questions to provide a thorough understanding of this vital nutrient.
The Importance of Vitamin D3
Chemical Structure and Synthesis
Vitamin D3 is a steroid hormone precursor that is synthesized in the skin when it is exposed to sunlight. It undergoes a series of metabolic processes in the liver and kidneys to form the biologically active form of Vitamin D, known as calcitriol. Calcitriol then acts on various tissues and organs throughout the body to regulate calcium and phosphate metabolism.
Biological Functions
Vitamin D3 has diverse biological functions, including
- Calcium Absorption: It enhances the absorption of calcium from the intestines, which is essential for maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis.
- Bone Mineralization: Vitamin D3 promotes the mineralization of bone tissue, ensuring that bones remain strong and healthy.
- Immune Modulation: It modulates the immune system, helping to prevent infections and reduce inflammation.
- Cell Growth and Differentiation: Vitamin D3 plays a role in cell proliferation and differentiation, which is important for tissue repair and regeneration.
- Regulation of Gene Expression: It regulates the expression of genes involved in various physiological processes, including those related to cell growth, metabolism, and immune function.
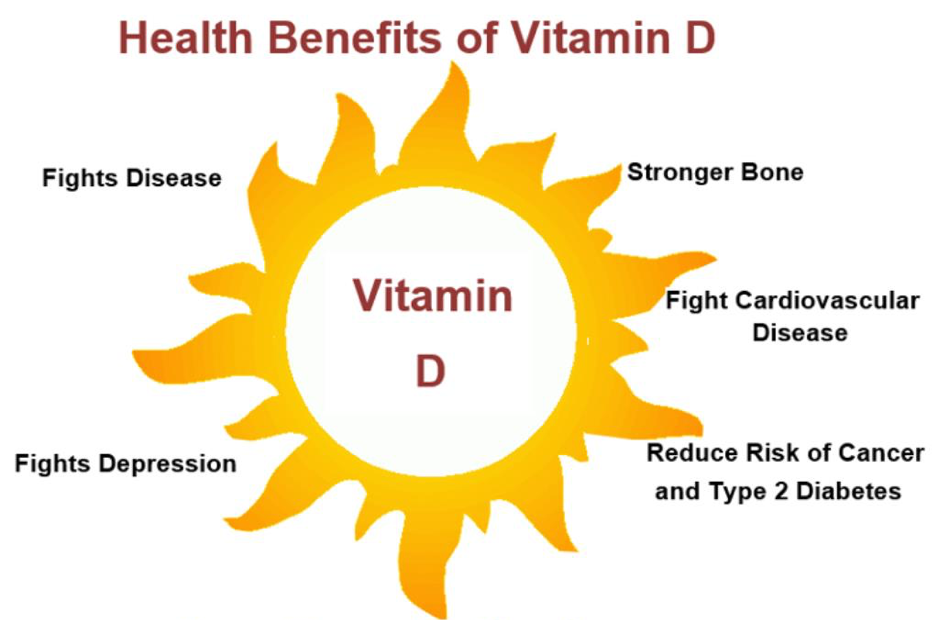
Health Benefits of Vitamin D3
Supports Bone Health
Vitamin D3 is essential for bone health as it helps regulate calcium and phosphate levels in the body. Adequate Vitamin D3 levels are necessary for proper bone mineralization and the prevention of bone diseases such as osteoporosis and rickets.
Boosts Immune Function
Vitamin D3 plays a critical role in immune function, helping to protect against infections and regulate the immune response. It enhances the activity of immune cells such as T cells and macrophages, which are involved in fighting off pathogens.
Supports Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin D3 may have protective effects on cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. It helps regulate blood pressure, improve endothelial function, and reduce inflammation in the cardiovascular system.
Enhances Mood and Mental Health
Low levels of Vitamin D3 have been linked to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. Supplementing with Vitamin D3 may help improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression, and enhance overall mental well-being.
Supports Muscle Function
Vitamin D3 plays a role in muscle function and strength, which is important for overall mobility and physical performance. Adequate Vitamin D3 levels may help prevent muscle weakness, falls, and fractures, particularly in older adults.
Sources of Vitamin D3
Sun Exposure
The primary source of Vitamin D3 is sunlight. When the skin is exposed to UVB radiation from the sun, it synthesizes Vitamin D3. Factors such as skin pigmentation, latitude, time of day, and sunscreen use can affect the amount of Vitamin D3 produced.
Dietary Sources
While Vitamin D3 is found in some foods, it is not abundant. Good dietary sources of Vitamin D3 include fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and tuna), egg yolks, fortified foods (such as milk, orange juice, and cereal), and supplements.
Recommended Intake of Vitamin D3
Daily Recommended Intake
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin D3 varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. The Institute of Medicine (IOM) recommends the following daily intake levels:
- Infants (0-12 months): 400 IU (10 mcg)
- Children (1-18 years): 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults (19-70 years): 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults (71 years and older): 800 IU (20 mcg)
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: 600 IU (15 mcg)
Factors Influencing Vitamin D3 Needs
Several factors can affect an individual’s Vitamin D3 requirements, including age, skin pigmentation, geographic location, season, and sun exposure habits. Individuals with limited sun exposure, darker skin, or certain medical conditions may require higher Vitamin D3 intake levels.
Symptoms of Vitamin D3 Deficiency
Common Signs and Symptoms
Vitamin D3 deficiency can lead to a range of symptoms, including
- Bone pain or tenderness
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue or tiredness
- Mood changes, such as depression or anxiety
- Impaired wound healing
- Increased susceptibility to infections
Health Risks of Deficiency
In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, Vitamin D3 deficiency can increase the risk of various health conditions, including osteoporosis, fractures, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, and certain cancers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Vitamin D3
Can I get enough Vitamin D3 from sunlight alone?
While sunlight is the primary source of Vitamin D3, factors such as skin pigmentation, geographic location, time of day, and sunscreen use can affect Vitamin D3 synthesis. In some cases, dietary supplements may be necessary to meet Vitamin D3 requirements.
Are there any risks associated with Vitamin D3 supplementation?
Vitamin D3 supplementation is generally safe when taken within recommended dosage levels. However, excessive intake of Vitamin D3 supplements can lead to toxicity, which may cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, weakness, and kidney damage.
Can Vitamin D3 prevent or treat COVID-19?
While some studies have suggested a potential link between Vitamin D3 levels and COVID-19 outcomes, more research is needed to determine whether Vitamin D3 supplementation can prevent or treat COVID-19 infections.
Can Vitamin D3 help with weight loss?
While some studies suggest a potential link between Vitamin D3 levels and weight management, evidence on the direct role of Vitamin D3 supplementation in weight loss is inconclusive. However, maintaining adequate Vitamin D3 levels may support overall metabolic health and contribute to a healthy weight.
Are there any natural ways to increase Vitamin D3 levels?
Aside from sunlight exposure and dietary sources, certain lifestyle factors can help maintain optimal Vitamin D3 levels. These include spending time outdoors, consuming Vitamin D3-rich foods, and incorporating Vitamin D3 supplements if necessary.
Can Vitamin D3 deficiency affect dental health?
Emerging research suggests that Vitamin D3 deficiency may be associated with an increased risk of dental problems such as periodontal disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss. Adequate Vitamin D3 levels may support oral health by promoting gum health and supporting tooth mineralization.
How long does it take to correct Vitamin D3 deficiency with supplementation?
The time it takes to correct Vitamin D3 deficiency with supplementation varies depending on the severity of the deficiency, individual factors, and the dosage of Vitamin D3 supplements. In general, it may take several weeks to months of consistent supplementation to restore optimal Vitamin D3 levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Vitamin D3 is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in various aspects of health, including bone health, immune function, cardiovascular health, mood regulation, and muscle function. Adequate Vitamin D3 levels are essential for maintaining overall well-being and reducing the risk of various health conditions. While sunlight exposure and dietary sources are important for Vitamin D3 intake, supplementation may be necessary for individuals at risk of deficiency. By understanding the benefits of Vitamin D3 and ensuring adequate intake, individuals can support their health and vitality.
- Xela Rederm Skin Booster Treatments Near Pyrford, Surrey - January 5, 2025
- Traptox Aka Trapezius Botox Treatment Near Capel, Surrey - January 4, 2025
- Skin Injectables Near Leigh, Surrey - January 3, 2025